Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures
Background
Defined by fracture of distal aspect of humerus above the epicondyles
Mechanism
Direct: blow to the elbow, fall onto flexed elbow
Indirect (more common): FOOSH, fall onto hyperextended UE
95% of these fractures are due to extension injury
Most common age: 5-8 year olds
Also more likely to be dislocated in this age group
Males>Females
Exam
Complain of pain/swelling/decreased ROM of elbow
“S shaped deformity”
when fracture is entirely displaced (distal humerus)
Need to perform neurovascular exam!
Median nerve: A-OK sign
Mostly commonly affected
Radial nerve: thumbs up sign
Ulnar nerve: abduct/adduct fingers (try to remove paper they are holding in between adducted fingers)
Check for cap refill!
Evaluate brachial artery
Compromise of the artery can lead to permanent volkmans contracture, which is flexion at the wrist
Gartland Classification
Based on the integrity of the cortex and extent of displacement
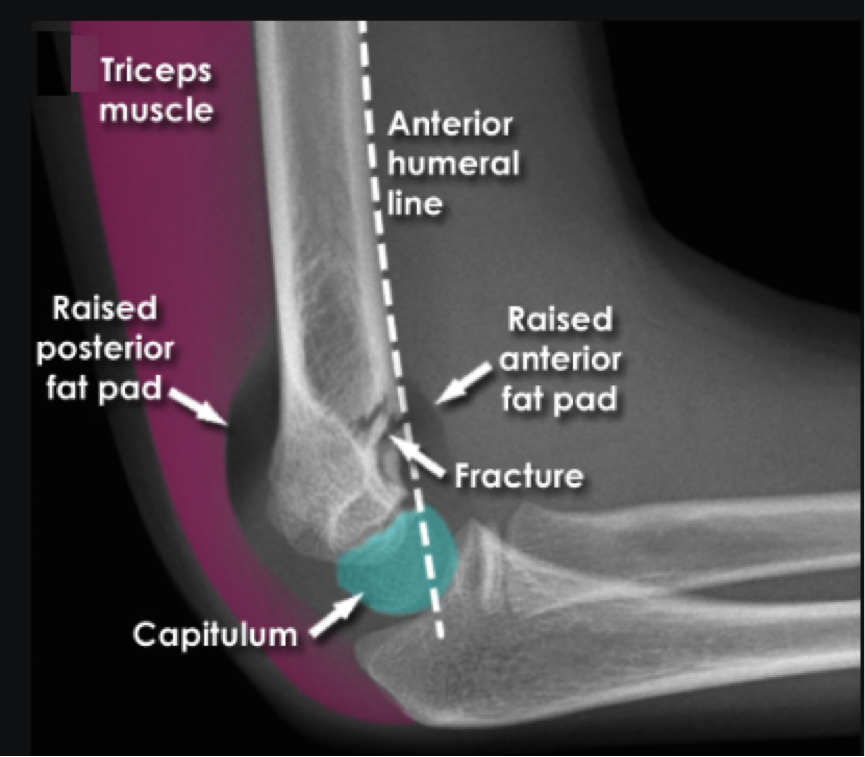
Type 1: minimal to no displacement ; limited XR findings, look for occult signs of fx on xray (ie: fat pad)
Type 2: posterior hinge aka displaced anterior wall but intact posterior wall; anterior humeral line is anterior to capetellum
Type 3: complete displacement with no cortices in tact, neither anterior nor posterior wall in tact
Type 4: periosteal disruption with instability in extension AND flexion
Imaging
Need AP and lateral films
Lines
Abnormality can indicate occult fracture
Radiocapitellar line (yellow): Line through central radius and central capitellum (middle third). Should be evaluated in both views
Anterior humeral line (blue): Line in front of the humerus and passes the anterior 1/3 of the capitellum.
Fat pads
Anterior: can be normal; elevation is abnormal
Posterior: always pathologic
These abnormalities without obvious sign of fracture along bones indicative of type 1 SC fx
Dispo:
Type 1: long arm posterior splint, ortho follow up
Type 2/3: OR with ortho for reduction (closed vs. open) and pinning