What's the deal with blasto?
Blastomycosis
Infection comes from inhalation of Blastomyces dermatitis or Blastomyces gilchristii
Endemic to soil in Great Lakes, Ohio, Mississippi and Saint Lawrence River valleys
And now emerging in upstate New York!
Infection
May be asymptomatic, flu-like illness, to respiratory failure and death
Lung (91%)
Symptoms: cough, fever, sputum production, chest pain, shortness of breath, weight loss, night sweats, chills, hemoptysis
Can present as acute or chronic pneumonia that does not respond to treatment
May lead to ARDS
Extrapulmonary disease
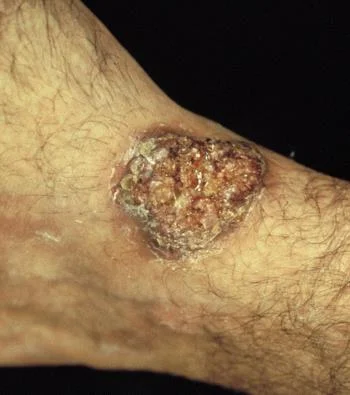
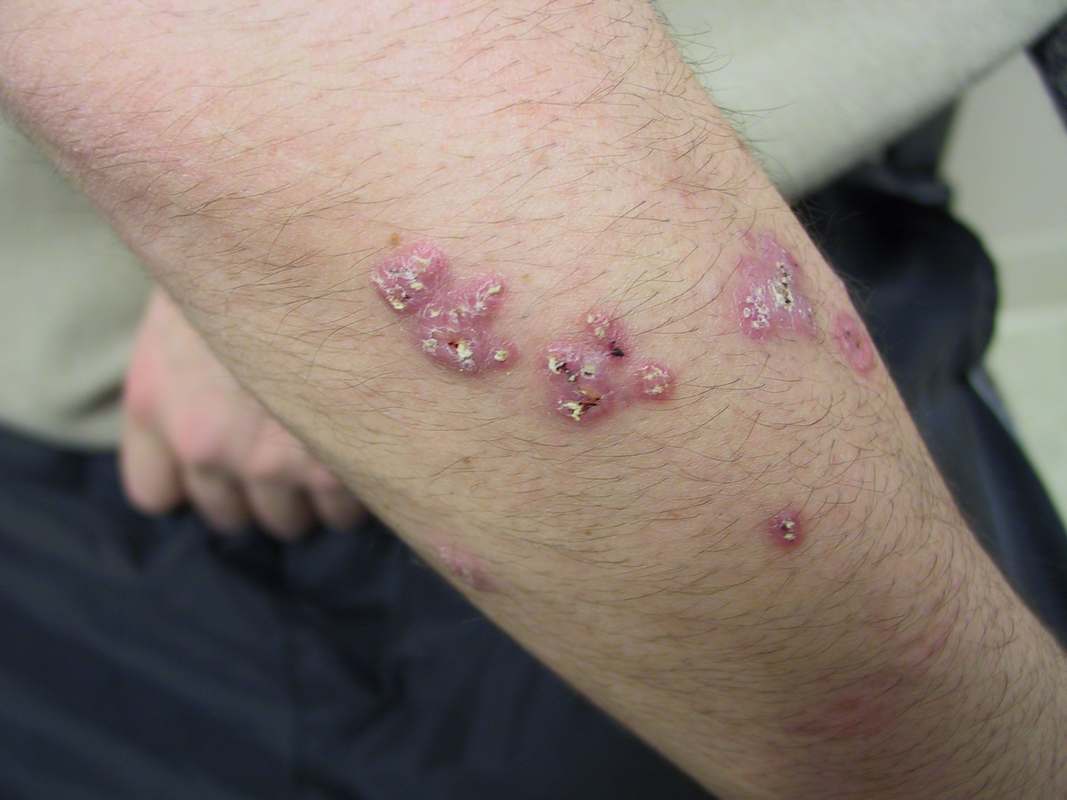
Skin (18%) - gray to violet verrucous lesions with irregular boarders
may be mistaken for pyoderma gangrenosum or squamous cell carcinoma
Diagnosis
Urine and serum antigens (urine more sensitive), high cross reactivity with histoplasmosis
Histologic visualization of yeast on sputum, tissue, or purulence sample
Culture (sputum cultures often contaminated with bacteria that will inhibit growth so should also be cultured on medium with chloramphenicol)
CT - nodules, consolidation w/ or w/out cavitation, tree-in-bud opacities, LACK of significant hilarity adenopathy (distinguishes it from histoplasmosis)
Treatment
Severe: Amphotericin B 3-5mg/kg daily for 1-2 weeks until improvement noted, then Itraconazole 200mg TID x 3 days then BID for 6-12 months
Moderate to mild: Itraconazole 200mg TID x 3 days then BID or QD for 6-12 months
Can use fluconazole or ketoconazole but less effective