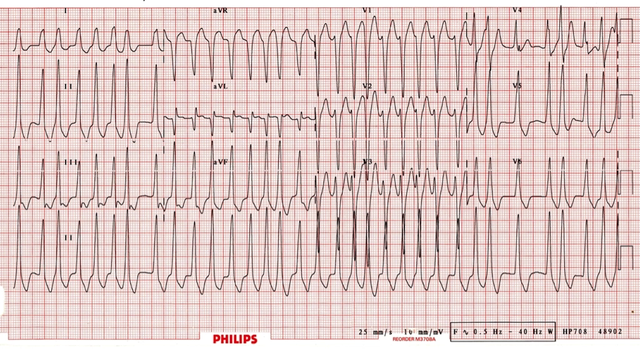
Atrial fibrillation can occur in up to 20% of patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome (WPW). The accessory pathway allows for rapid conduction directly to the ventricles bypassing the AV node. Rapid ventricular rates may result in degeneration to VT or VF.
ECG features of Atrial Fibrillation in WPW are:
Rate > 200 bpm, can be closer to nearly 300bpm!
Irregular rhythm
Wide QRS complexes due to abnormal ventricular depolarization via accessory pathway
QRS Complexes change in shape and morphology
Axis remains stable unlike Polymorphic VT
Treatment
Treatment with AV nodal blocking drugs e.g. adenosine, calcium-channel blockers, beta-blockers may increase conduction via the accessory pathway with a resultant increase in ventricular rate and possible degeneration into VT or VF
In a hemodynamically unstable patient urgent synchronized DC cardioversion is required.
Medical treatment options in a stable patient include procainamide, although DC cardioversion may be preferred.
Example of EKG of WPW with afib
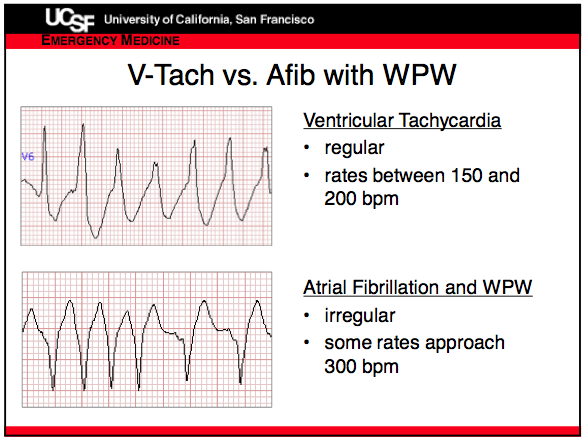
Vtach vs Afib in WPW