Here is this week's VOTW:
A 69-year old male with a history of COPD presented to the ED for 1 month of cough and 1 week of hemoptysis. A chest x-ray showed a left lower lobe consolidation vs atelectasis vs effusion. A POCUS was performed to better characterize the area which showed…
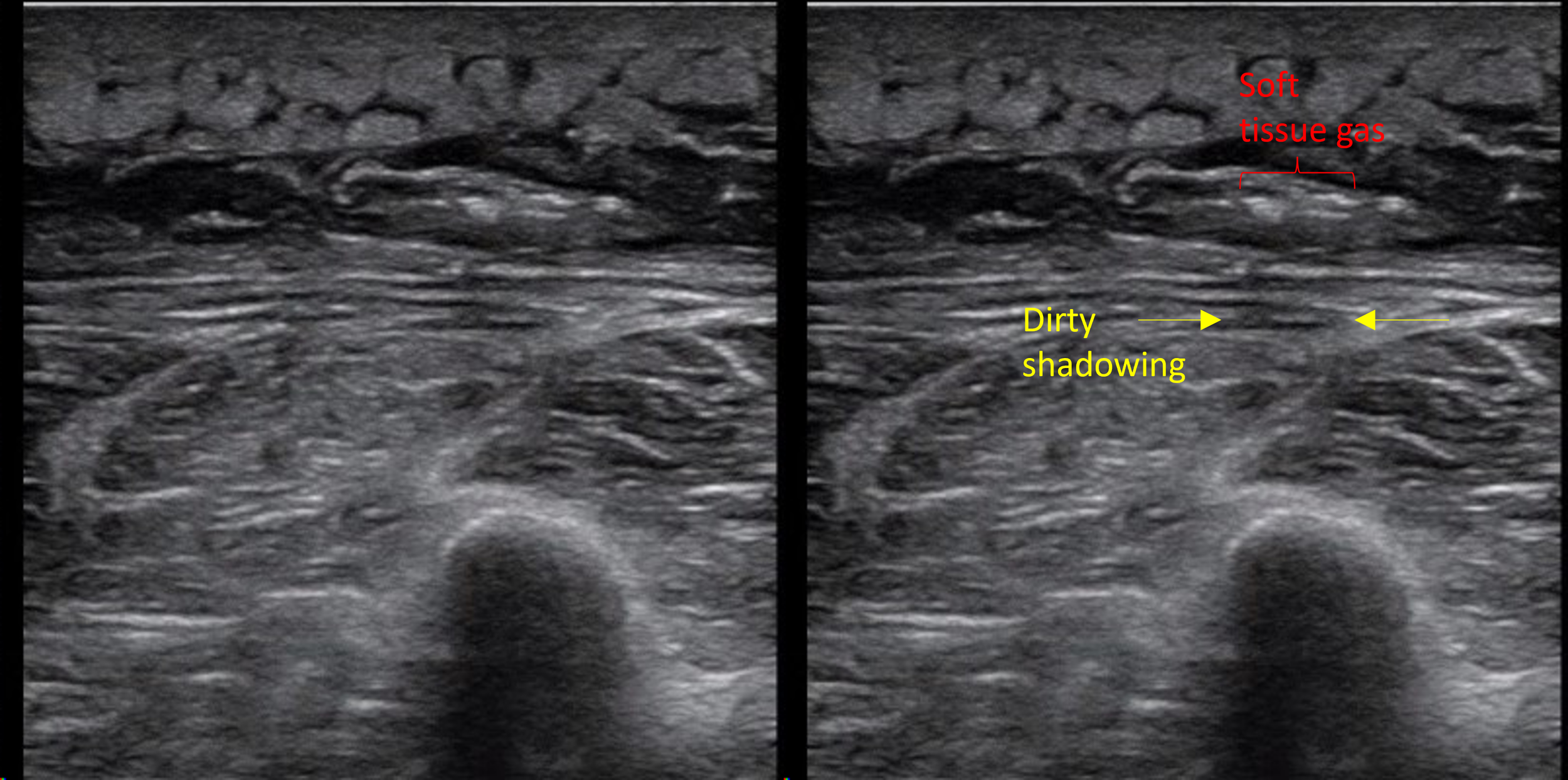
Clip 1 and Clip 2 shows "hepatized lung", a large isoechoic area of lung tissue just under the pleura that has a similar echogenecity to the liver which is suggestive of a consolidation. The echogenic jagged line in the far field is the interface between consolidated and aerated lung. Within the consolidation, air bronchograms (scattered echogenic dots and lines) can be seen.
Findings of pneumonia on lung ultrasound
Hepatization of the lung - Normal lung tissue is not visible on ultrasound as it is filled with air. As pneumonia develops, inflammatory material (fluid, pus) fill the alveoli of the lung, and the affected lung tissue becomes more solid and visible on ultrasound. A large consolidation takes on the appearance of a solid organ like liver and is referred to as “hepatization of the lung”. Atelectasis can also have this appearance.
B-lines are not specific to pulmonary edema and can be see with pneumonia due to the fluid within the alveoli. This may be the only finding in early pneumonia. Focal B-lines are more suggestive of infectious process while diffuse B-lines are more suggestive of pulmonary edema.
Shred sign refers to small hypoechoic lesions abutting the pleura which gives the appearance of a jagged pleural line. This is highly specific for a small subpleural consolidation. The jagged line is the interface between consolidated and aerated lung and not actually the pleural interface.
Air bronchograms (image below) are small pockets of air that are present within the small bronchi within the consolidation seen in both atelectasis and consolidation. Dynamic air bronchograms move in and out along the bronchi with each breath and is more specific for a true consolidation. Static air bronchograms are more suggestive of atelectasis as with complete collapse of the lung air won’t move in or out but can also be seen with consolidation.
Image 1. Air bronchograms
Pleural effusions frequently accompany a pneumonia. Echogenic debris or septations within the effusion can suggest an empyema.
Tips and tricks on Lung Ultrasound
Use the curvilinear probe using the Lung settings
Orient your probe with the probe marker towards the head, find two ribs which are hyperechoic with posterior shadowing and identify the shiny shimmering pleura in between
If looking for B-lines, increase the depth so you can see the b-lines which extend all the way down the screen. This lets you differentiate B-lines from comet tail artifacts which do not extend all the way down the screen and are not pathologic.
If looking for a pneumothorax, decrease the depth so you can focus at the pleura and more easily look for lung sliding. You can also switch to a linear probe for higher resolution
When looking for a pleural effusion at the lung bases, bring the vertebral bodies in view so that you can look for a “spine sign” (extension of the spine above the diaphragm which would indicate the presence of a pleural effusion)
Case conclusion
A CTA Chest showed a dense left lower lobe consolidation. The patient was given IV antibiotics and admitted for the management of pneumonia and hemoptysis.
Here is a great review of lung ultrasound for pneumonia: https://litfl.com/lung-ultrasound-pneumonia/
Happy Scanning,
Your Sono Team