For this pearl of the day we will talk about systematic approach to reading CXR and hidden pneumonias:
The key is to be very systematic when approaching CXRs and that is what radiologists do each time.
Here is the suggested approach by the Brown EM program (https://brownemblog.com/?offset=1533674064239&category=Education)
When ready to review the x-ray, consider the commonly used “A, B, C, D, E, F” system.
A - Airway- trachea, carina, right and left main bronchi
B - Bones and soft tissue- clavicles, ribs- posterior and anterior, vertebral bodies, and sternum on lateral films. Look for any fractures, dislocations, or lytic lesions.
C - Cardiac- cardiac silhouette and mediastinum. The cardiac silhouette should be less than half of the thoracic cavity. AP films exaggerate heart size, so this rule does not apply. Assess the borders of the heart and the hilar structures
D - Diaphragm- right should be higher than left and you should see a gastric air bubble on the left. Is there any free air under the diaphragm? Evaluate the costophrenic angle and pleura (normally invisible due to thinness).
E - Everything else (lines and tubes, pacemakers, artificial valves)
F - Fields- FINALLY, evaluate the lung fields. Lungs are the area of greatest interest, so it is helpful to keep this at the end to prevent distraction. Divide each lung into three “zones” when reading a chest x-ray. These do not correlate with the lobes. Remember, there are 2 lobes on the left (upper and lower) and 3 on the right (upper, middle and lower).
Hidden pneumonias:
Go through your ABCDEFs and look at the signs of hidden pneumonias:
Silhouette sign
The loss of the normal silhouette of a structure is called the silhouette sign. - It enables us to find subtle pathology and to locate it within the chest.
R middle lobe pneumonia
LLL pneumonia
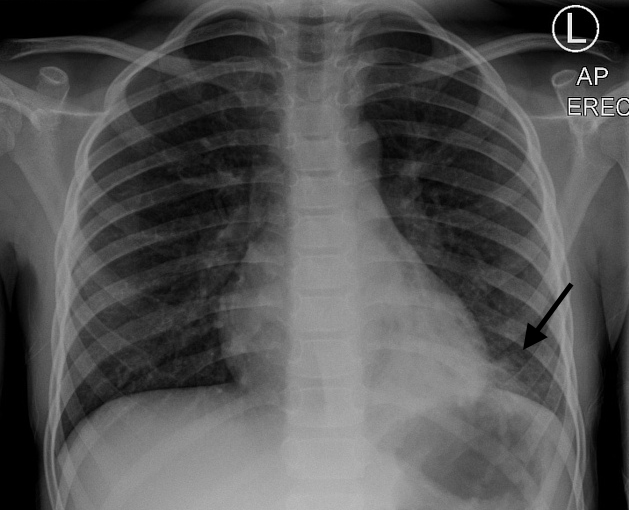
LLL pneumonia
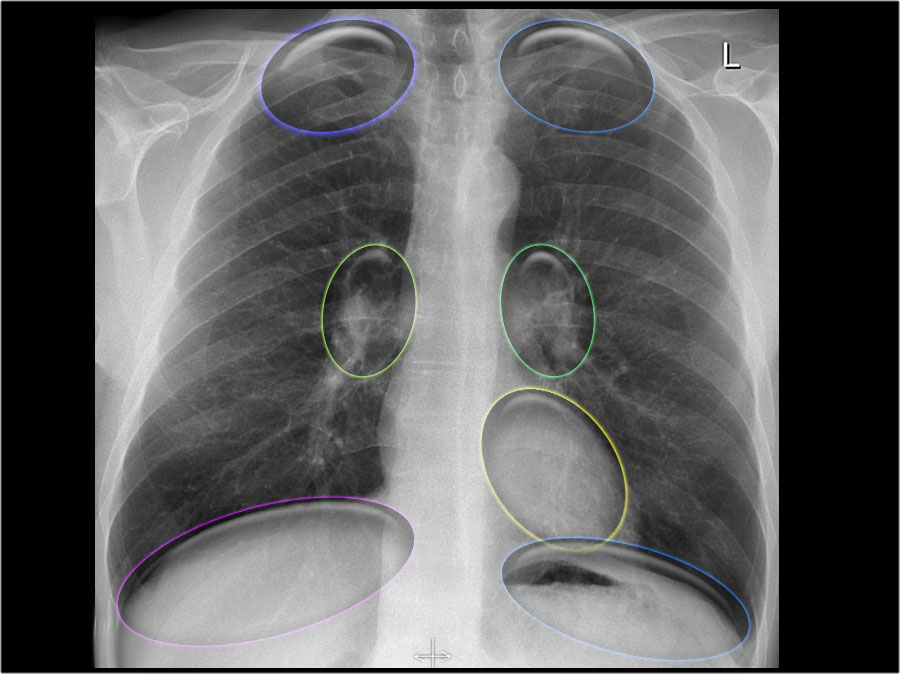
Hidden areas
There are some areas that need special attention, because pathology in these areas can easily be overlooked:
apical zones
hilar zones
retrocardial zone
zone below the dome of diaphragm
These areas are also known as the hidden areas.
But in doubt get another view or a chest CT.
References:
https://brownemblog.com/?offset=1533674064239&category=Education